Postal codes are essential components of every mailing address, helping postal systems around the world sort and deliver packages accurately. Despite serving the same function, the terms ZIP code and postcode are not interchangeable.
While the US uses the term ZIP code, countries like the UK and others refer to it as a postcode. This blog explores the key differences between the two, explaining their formats, usage, business relevance, and more.
If you’ve ever wondered whether they’re the same or what separates them, here’s your detailed answer.
What Is a Postal Code?
A postal code is a coding system used globally to identify specific regions, districts, or delivery routes. It helps facilitate the efficient sorting and delivery of mail and parcels by both public and private courier services.
Postal codes can be numeric, alphabetic, or alphanumeric, depending on the country’s system. For instance, the UK use alphanumeric postcodes, while other countries may stick to numeric formats. (Example Postal Code: PO Box 5622 Manchester)
The main role of a postal code is to simplify logistics by narrowing down the recipient’s location, reducing the chances of delivery errors. Countries such as the UK, Saudi Arabia, Australia, and Germany all use postal codes, though the naming and structure vary.
Whether referred to as a postcode, ZIP code, or another term, it plays a fundamental role in making mail and logistics systems work seamlessly. Despite similarities, how these codes are structured and used can differ dramatically from one country to another.
What Is a ZIP Code?
ZIP code stands for Zone Improvement Plan code. Introduced in the United States in 1963, it revolutionised the American postal system by allowing for more efficient mail sorting and faster deliveries. A ZIP code is a five-digit number used to indicate specific geographic regions in the United States and the Philippines.
The first digit represents a broad area of the country. The second and third digits further narrow it down to a city or region, and the fourth and fifth digits identify the local post office. In 1983, the ZIP+4 code was introduced to increase accuracy even further.
This format adds four more digits to the base ZIP code, helping to identify a more precise location such as a building or apartment floor.
The ZIP code system segments the country into mailing zones, making it easier for mail carriers to plan efficient delivery routes. It’s an essential tool for logistics, demographics, and business operations across the United States.
How Do Postcodes and ZIP Codes Differ in Structure?
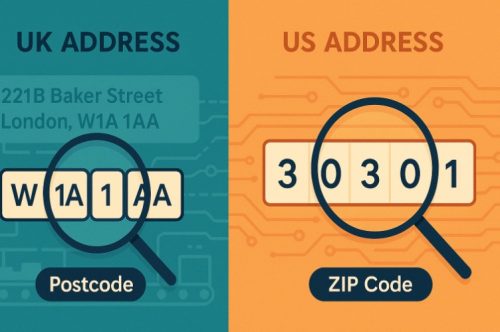
Although ZIP codes and postcodes serve a similar purpose, their structures differ in design and complexity. These differences affect how mail is processed and delivered in different countries.
Key Format Differences:
- ZIP Codes: Primarily five-digit numbers, sometimes extended to ZIP+4 with an additional four digits for precision.
- Postcodes (UK): Alphanumeric and typically include two parts, the outcode and the incode, separated by a space.
Example Breakdown:
- ZIP Code Example: 90210 (Beverly Hills, California)
- Postcode Example: SW1A 1AA (London, UK)
Summary of Differences in Bullet Points:
- ZIP codes are numeric; postcodes are alphanumeric.
- ZIP codes cover general zones; postcodes target precise delivery points.
- ZIP codes follow a 5-digit format; UK postcodes can range from 6 to 8 characters.
- Postcodes provide a higher level of location granularity, especially in dense urban areas.
Understanding these differences is key when sending mail internationally or using postal data in business systems.
Why Do Countries Use Different Formats for Postal Codes?
Postal code formats vary globally due to several key reasons. Each nation has developed a system that reflects its geographical, administrative, and logistical requirements. Below is a breakdown of the primary reasons.
Geographic Considerations
Countries with large land masses like the United States use numeric ZIP codes to segment massive areas into manageable zones. In contrast, countries with dense urban populations, like the UK, require more detailed alphanumeric systems to pinpoint delivery points precisely.
Administrative Structures
Governments structure postal codes around local administrative boundaries. The UK’s Royal Mail built its system to include district and sector identifiers, while the US Postal Service based its model on delivery routes and state divisions.
Technological and Operational Efficiency
Countries design their systems to integrate with automated mail-sorting technology. A unique format ensures each nation can process large volumes of mail accurately and quickly.
For instance, the alphanumeric postcode in the UK assists machines in routing post efficiently even within a single city block.
Language and Cultural Adaptability
Some countries may incorporate alphabetic characters in their postal codes to reflect local language systems or to improve ease of use in native scripts, further contributing to variation worldwide.
Are Postal Codes and ZIP Codes Used Interchangeably Worldwide?
Although they serve similar roles, postal codes and ZIP codes are not universally interchangeable. The term ZIP code is specific to the United States and the Philippines, where it is officially adopted and used by their postal systems. In contrast, postal code is a generic, internationally accepted term used across the globe.
Countries like the UK, Canada, and Australia use the term postcode, which is a type of postal code. Despite these naming differences, the core function remains consistent: aiding in the accurate sorting and delivery of mail.
However, when filling out international forms or shipping across borders, it’s essential to use the correct term and format relevant to the destination country. This ensures proper processing and reduces the risk of misdelivery.
Why Do ZIP Codes Focus on Delivery Routes While Postcodes Target Geographic Areas?
ZIP codes and postcodes are both essential for mail delivery, but their design priorities differ. ZIP codes are built around delivery routes, while postcodes focus more on identifying specific geographic regions.
ZIP Code Logic
- Structured to optimise mail delivery efficiency across routes.
- Divides entire states and cities into manageable delivery zones.
- ZIP+4 codes narrow down delivery to buildings or departments.
Postcode Logic
- Designed around administrative and geographical boundaries.
- Helps determine physical areas like boroughs, sectors, and streets.
- Every UK postcode corresponds to an exact location or a small group of properties.
Summary:
- ZIP codes improve carrier route efficiency by mapping delivery paths.
- Postcodes help identify real-world locations with high accuracy.
- This difference is a reflection of how each country’s mail infrastructure is set up and prioritised.
This distinction becomes even more relevant in dense metropolitan areas where delivery logistics and address validation are critical.
How Are Postal Codes Used Beyond Just Mailing Purposes?
Postal codes do more than just direct mail. In today’s digital and data-driven world, they provide valuable insights for various applications.
Insurance and Risk Analysis
Insurance providers use postal codes to assess risks such as crime rates, flood zones, or historical claim data. This helps determine pricing for home, auto, and health insurance premiums.
Data Analytics and Market Segmentation
Businesses analyse postal code data to identify sales hotspots and underserved areas. It helps them understand where their customers are and what marketing strategies may work.
These examples show how postal codes are evolving from basic mail identifiers into powerful tools for analytics and strategy.
What Role Do ZIP Codes and Postcodes Play in Business Operations?
ZIP codes and postcodes contribute significantly to operational efficiency in multiple business sectors. Beyond mailing, they impact logistics, customer experience, and data-driven decision-making.
- Enable accurate delivery estimation for e-commerce businesses.
- Help customer service teams verify address legitimacy.
- Assist in personalising offers and promotions based on location.
Benefits in Bullet Points:
- Enhance geotargeting for ads and campaigns.
- Reduce shipping errors and associated costs.
- Improve delivery turnaround time for couriers and retailers.
From fulfilment to after-sales service, postal codes power smooth and intelligent business operations.
Which Industries Rely Most on Postal and ZIP Code Systems?
Several industries depend heavily on ZIP codes and postcodes to function efficiently and competitively.
- E-commerce: Uses postal data to calculate shipping rates and delivery times.
- Logistics: Plans optimised delivery routes using geographic segmentation.
- Real Estate: Analyses location-based trends for property valuation.
- Insurance: Determines premiums by assessing postcode-related risk data.
Other Examples Include:
- Healthcare: For planning service coverage areas.
- Marketing: For demographic targeting and audience segmentation.
These industries rely on accurate postal information to streamline operations and provide better customer experiences.
What Tools Can You Use to Lookup and Validate Postal Codes?
Postal code lookup and address validation tools have become crucial for both businesses and individuals aiming to ensure precise deliveries.
Available Tools:
- Postal Code APIs: Allow real-time lookups and data validation.
- Address Verification Systems: Match the user-entered data against official postal databases.
- Autocomplete Features: Suggest valid address entries as the user types.
Features of These Tools:
- Recognise ZIP+4 and full postcode structures.
- Offer metadata like city, region, and delivery point info.
- Standardise addresses according to local postal standards.
Whether you’re sending mail or building a checkout form, these tools reduce errors and increase confidence in address-based processes.
Postal Code vs ZIP Code | Quick Comparison Table
While both ZIP codes and postcodes serve similar delivery functions, they differ in terminology, structure, usage scope, and management systems. Below is a comparison table for quick reference.
| Factors | ZIP Code | Postcode (UK) |
| Year Introduced | 1963 | 1857 (London), adopted in 1959 nationally |
| Format | Numeric (5 or 9 digits) | Alphanumeric (6–8 characters) |
| Region | US, Philippines | UK and other Commonwealth countries |
| Managed By | United States Postal Service | Royal Mail (UK) |
| Main Focus | Delivery route efficiency | Geographic area identification |
| Extra Function | ZIP+4 for precise building delivery | Delivery point validation |
Understanding these distinctions is crucial for correctly using these codes in international communication and commerce.
Conclusion
While postal codes and ZIP codes share the same foundational purpose of sorting and delivering mail, their structures, naming conventions, and applications vary by country.
ZIP codes are a product of the US postal system focused on delivery routes, while postcodes are detailed geographic identifiers used in the UK and other regions.
These codes have also expanded into business applications, enabling better logistics, marketing, risk analysis, and customer experience.
Knowing how and when to use the right term or tool can significantly impact the success of your communication and delivery processes.
FAQs About Postal Code vs ZIP Code
Where can I find the ZIP code or postcode of any location?
You can use address lookup APIs or official postal websites to find ZIP codes or postcodes for any location accurately.
How frequently do ZIP codes and postcodes change?
ZIP codes are updated based on population or logistical needs, while postcodes typically change every six months in the UK.
Can a single city have multiple ZIP codes or postcodes?
Yes, larger cities and even single buildings may have more than one ZIP code or postcode to manage mail volumes.
How do I convert a ZIP code to a postcode?
You can use geolocation or lookup tools to translate ZIP codes into the closest equivalent postcode format.
Why do some countries have longer postal codes than others?
Countries with dense populations or complex delivery zones use longer codes for more precise address targeting.
Are ZIP codes used outside the US?
ZIP codes are mostly used in the US and the Philippines; other countries have their own postal code systems.
How do postal codes support e-commerce and delivery services?
They allow businesses to calculate shipping costs, estimate delivery times, and validate customer addresses effectively.







